Leetcode 450 : Delete Node in a BST
Solution to Delete Node in a BST problem.
This solution is an easy to understand sub-optimal solution. Later, we will look at how to make it more performant. Given below is the steps followed,
Recursively find the node that has the same value as the key. Once the node is found, have to handle the below 4 cases
- Node doesn’t have left or right subtree - set node to null
- Node only has left subtree - set the node to the left subtree
- Node only has right subtree- set the node to the right subtree
- Node has both left and right - find the minimum value in the right subtree, set that value to the currently found node, then recursively delete the minimum value in the right subtree.
class Solution {
public TreeNode deleteNode(TreeNode root, int key) {
if (root == null)
return null;
if(root.val > key) {
root.left = deleteNode(root.left, key);
} else if(root.val < key) {
root.right = deleteNode(root.right, key);
} else {
// Found the node
if(root.left == null && root.right == null)
root = null;
else if(root.left == null)
root = root.right;
else if(root.right == null)
root = root.left;
else {
// both left and right are non-null
// find the min value from right and make it the current nodes value
int minVal = findMinFromtRightSubtree(root.right);
root.val = minVal;
// Now delete the min value from right as it was copied over
// in the previous step
root.right = deleteNode(root.right, minVal);
}
}
return root;
}
private int findMinFromtRightSubtree(TreeNode node) {
while(node.left != null)
node = node.left;
return node.val;
}
}The above approach copies value from one node to another. The next approach given below avoids this copying of value.
class Solution {
public TreeNode deleteNode(TreeNode root, int key) {
if(root == null)
return root;
return deleteNodeRecursively(root, key);
}
private TreeNode deleteNodeRecursively(TreeNode curNode, int key) {
if(curNode == null)
return curNode;
if(curNode.val == key) {
curNode = deleteNode(curNode);
} else if(key < curNode.val) {
curNode.left = deleteNodeRecursively(curNode.left, key);
} else {
curNode.right = deleteNodeRecursively(curNode.right, key);
}
return curNode;
}
private TreeNode deleteNode(TreeNode nodeToBeDeleted) {
if(nodeToBeDeleted.left == null && nodeToBeDeleted.right == null)
return null;
if(nodeToBeDeleted.right == null)
return nodeToBeDeleted.left;
if(nodeToBeDeleted.left == null)
return nodeToBeDeleted.right;
TreeNode inorderSuccessor = nodeToBeDeleted.right;
while(inorderSuccessor.left !=null) {
inorderSuccessor = inorderSuccessor.left;
}
inorderSuccessor.left = nodeToBeDeleted.left;
return nodeToBeDeleted.right;
}
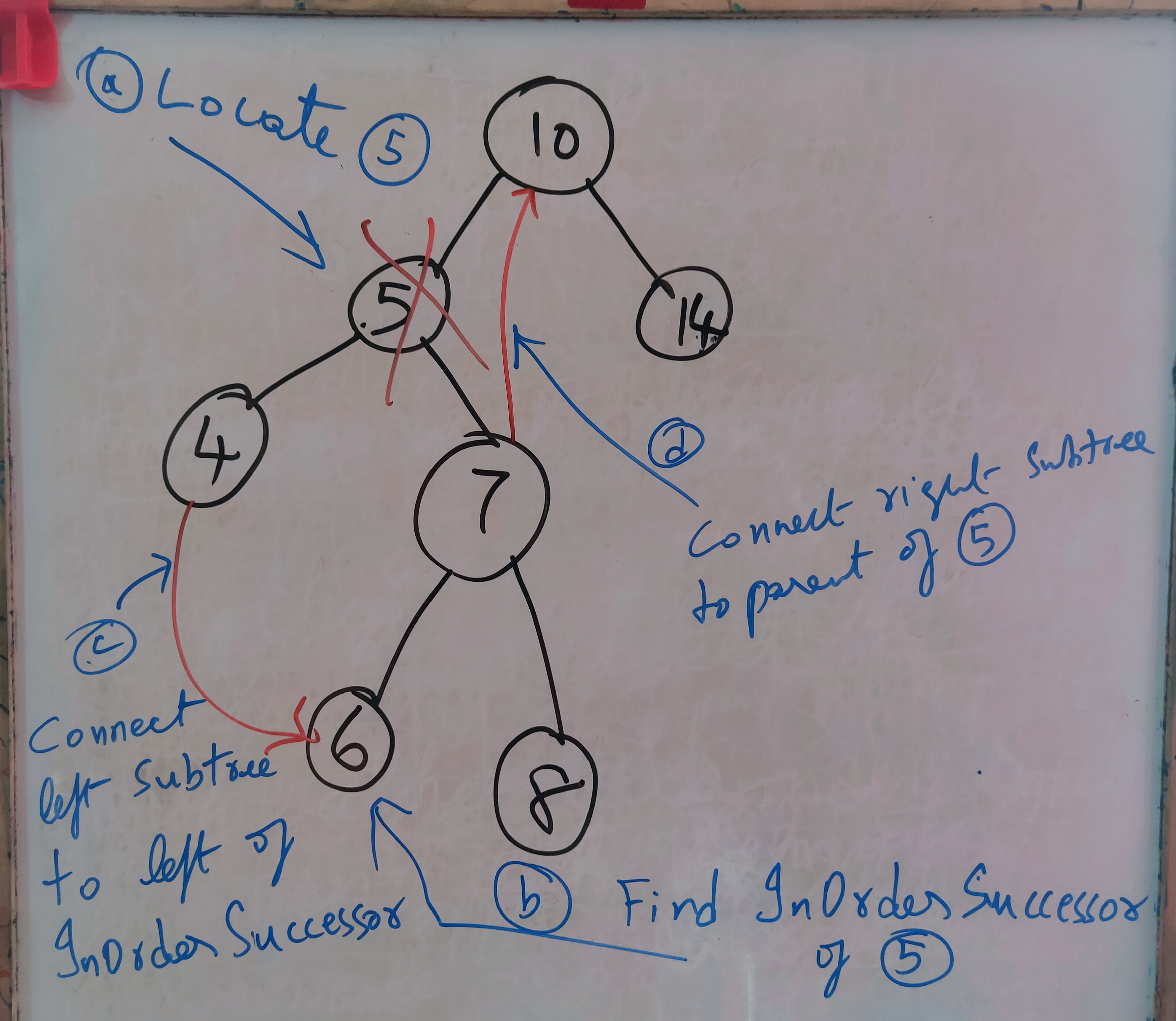
}The diagram below explains the steps followed to delete node (5) from the BST. Steps : (a) Locate node (5) (b) Find the inorder successor of (5) which is (6) (c) Connect the left subtree of (5), which is (4) here, to the left of inorder successor (d) Connect the right subtree of (5), which is (7) here, to the parent of (5)
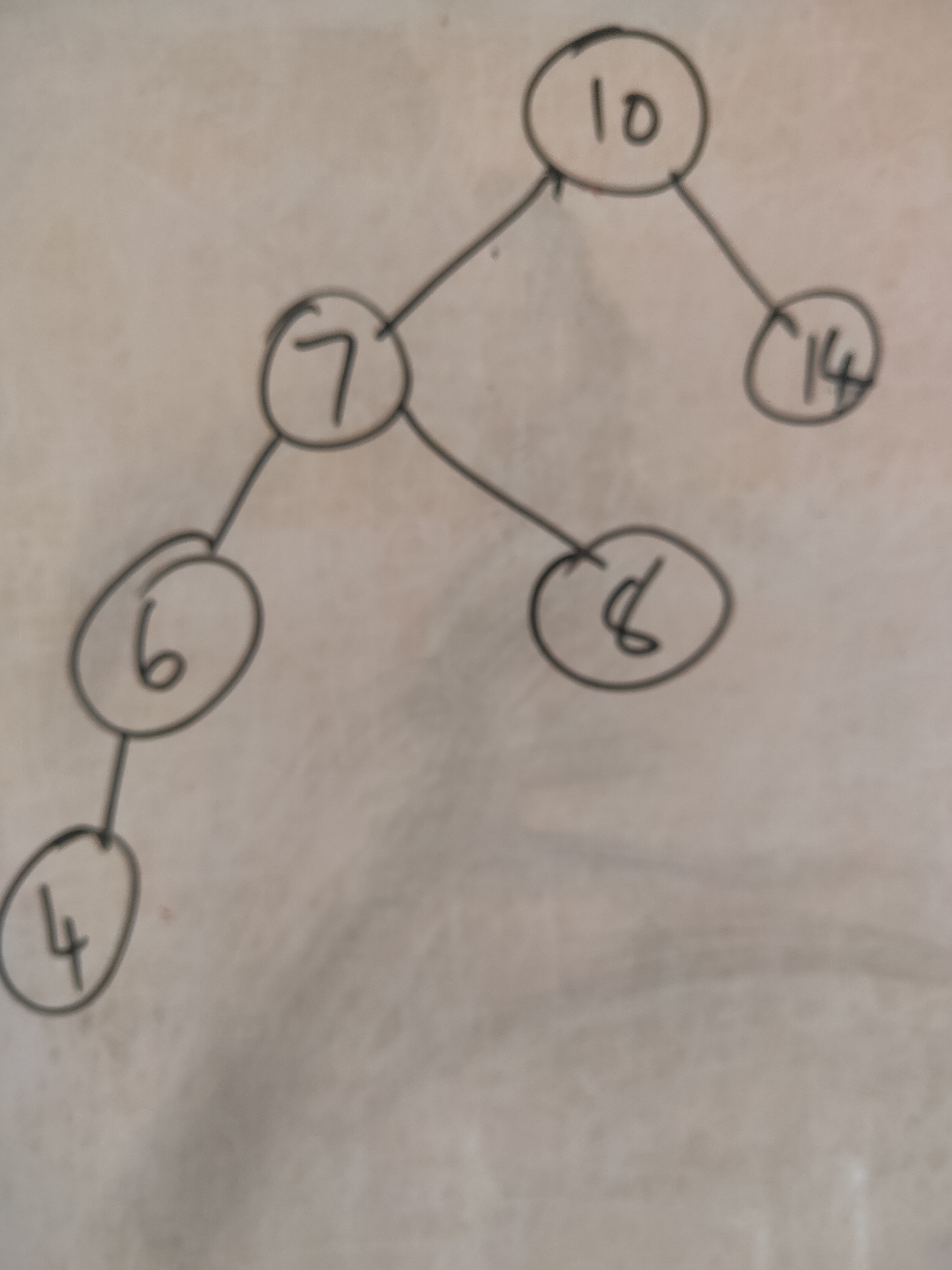
The diagram below shows the tree after the deletion of Node (5).